Architecture, Operation, and Benefits
Access control systems are essential for ensuring security and managing entry to buildings, areas, or resources. With advancements in technology, a variety of access control systems have been developed, each with unique architectures, operational methods, and benefits. Here is a detailed exploration of these technological options:
1. Traditional Access Control Systems
Architecture and Operation:
- Card-Based Systems: These systems use physical cards (such as magnetic stripe cards or proximity cards) that users swipe or present to a reader to gain access.
- Keypad Systems: Users enter a personal identification number (PIN) on a keypad to unlock doors or access points.
- Lock and Key Systems: The most basic form, where physical keys are used to open locks.
Benefits
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and use.
- Cost-Effective: Generally cheaper to implement initially.
- Reliability: Proven track record of functioning without complex technology.

2. Biometric Access Control Systems
Architecture and Operation:
- Fingerprint Scanners: Users place their finger on a scanner, which verifies their identity based on fingerprint patterns.
- Facial Recognition: Cameras capture and analyze facial features to allow or deny access.
- Iris Scanners: Scan the unique patterns in the iris of the user’s eye.
- Voice Recognition: Identifies users based on their voice patterns.
Benefits
- High Security: Difficult to forge or duplicate biometric features.
- Convenience: No need for physical keys or cards, reducing the risk of loss or theft.
- Audit Trails: Provides detailed logs of who accessed what and when.

3.Smart Card and Mobile Access Control Systems
Architecture and Operation:
- Smart Cards: Embedded with microchips that store data and communicate with readers via radio-frequency identification (RFID) or near-field communication (NFC).
- Mobile Credentials: Uses smartphones with NFC or Bluetooth technology to gain access. Users can use an app or digital wallet to manage their credentials.
Benefits
- Flexibility: Easy to update or revoke access permissions remotely.
- Integration: Can be integrated with other systems like time and attendance, or visitor management.
- User-Friendly: Most people are familiar with using smartphones, making adoption easier.
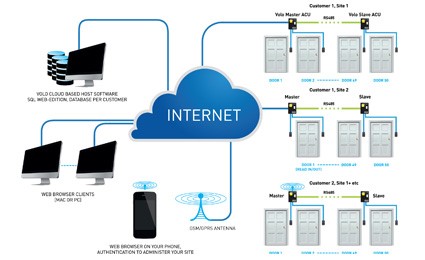
4. Cloud-Based Access Control Systems
Architecture and Operation:
- Cloud Management: Access control data and management are hosted on a remote server, accessible via the internet.
- IoT Integration: Devices connected through the Internet of Things (IoT) allow for remote control and monitoring.
Benefits
- Scalability: Easily scale up or down depending on the organization’s needs.
- Remote Access: Administrators can manage the system from anywhere, improving response times and flexibility.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure and maintenance.
4. Cloud-Based Access Control Systems
Architecture and Operation:
- Behavioral Biometrics: Monitors patterns such as typing rhythm, gait, and other behavioral characteristics.
- Predictive Analytics: Uses data to predict potential security breaches and suggest preventative measures.
- Adaptive Security: Continuously learns and adapts to new threats and changing conditions.
Benefits
- Proactive Security: Identifies and mitigates threats before they occur.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Reduces false positives and negatives by continuously learning and improving.
- Personalization: Tailors security measures to individual behaviors, improving user experience.
Benefits of Advanced Access Control Systems
- Enhanced Security: Modern systems offer higher security through multi-factor authentication, biometrics, and advanced encryption.
- Convenience and Efficiency: Streamlines the process of granting and revoking access, reduces administrative overhead, and simplifies user interactions.
- Integration Capabilities: Can be integrated with other security systems (e.g., CCTV, alarm systems) and business systems (e.g., HR, visitor management).
- Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting: Provides real-time data and analytics on access events, helping in quick decision-making and incident response.
- Cost Savings: While the initial investment might be higher, advanced systems can reduce long-term costs through decreased need for physical security measures and improved operational efficiency.
- Compliance: Helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements regarding security and data protection.
Conclusion
Access control systems have evolved significantly with technological advancements, offering various options to meet different security needs. From traditional systems to cutting-edge AI-driven solutions, each type of system comes with its own set of architectures, operational methodologies, and benefits. Selecting the appropriate access control system depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the organization, with an eye towards future scalability and integration capabilities.
